Redundant Array of Independent/ Inexpensive Disks keeps your data stored on various hard disks. It saves the data in case of any mishap. It also improves the performance and reliability of storage devices. Raid allows the users to utilize more than one hard disk. It will be great for speeding up the computer. Different varieties of Raids are present in the market, like Raid 0, Raid 1, etc.
5 Types of Raid Support on Motherboard
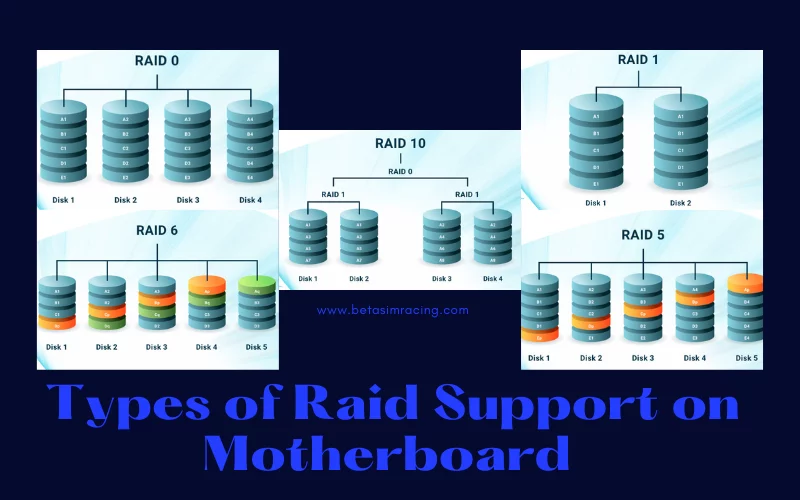
There are some levels or types of Raid. You can install them as you need.
1) Raid 0
Raid system for PC depends on users’ needs. If you use Raid 0, it means you save your data in two hard drives. The one in your device and the one additionally applied to do this. It will divide the data into both drives. The danger is that your data will be entirely corrupted if the two hard drives fail.
2) Raid 1
Raid 1 divides all the available hard drives equally. It will give one-one pair of two hard drives. If you have 4 hard drives, then it will help in making two-two pairs. Raid 1 offers to store the data copy in the other drive. It results in a backup of the data if the hard drives fail.
3) Raid 10
Raid 10 is an operation of Raid 0 and Raid 1. It takes Raid 0 benefit as good drive speed and Raid 1 benefit as data backup. Here you can use a minimum of four hard drives. Here a pair of drives receive data and other forms it is mirroring. It will get speedy function and backup coverage.
4) Raid 5
Raid 5 offers to store data in parts, but it strips with parity across drives. If any hard drive fails to perform, then your data can be recovered because other hard drives rebel the data perfectly.
5) Raid 6
Raid 6 strips with dual parity across drives. If any drive fails, then the data can be recovered. It has a slow speed, so it needs a Raid controller. If the data is lost, then the process of recovery will take much time.
Features of Raid Support
Many organizations use top Raid systems for increased reliability. Raid can also be used in video editing, music production, and more. The volume size of the drives can increase the durability of the system.
There are some specific terms related to Raid that need to be understood.
- Parity: It is the way of distributing data across more drives to aid with low distribution and recovery of data if something goes wrong.
- Redundancy: In computer science, it is the duplication of all components. If one component goes down, the whole system does not fail.
- Mirroring: The replication of data from one drive to another is called mirroring. It exhibits precisely the same information for the best recovery.
- Striping: It is the way of writing data across many drives. The data will be divided in sequential order and distributed equally on all devices.
- Hot Spare: It is a spare disk used in place of any defective disk.
- Degraded Mode: When any drive fails to work, it works with parity on other devices. Raid’s performance will decrease, and it will be in degraded mode.
How to Setup Raid 0 in BIOS?
You will open up the BIOS menu and go down to integrated peripherals. Onboard SATA must be enabled with Raid. Save the changes. It will change the CMOS of the computer. Reboot the system. Now you will see a Raid configuration screen.
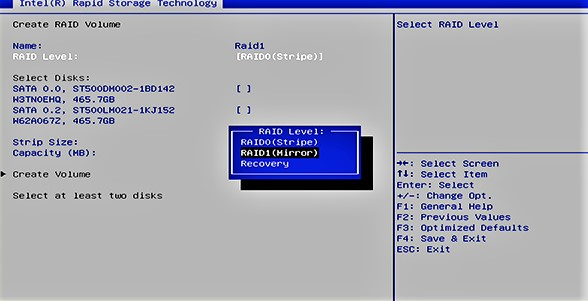
Choose to create a Raid disk drive. Here you will enter the Raid name. See its level and other information. Save the changes by pressing Y. On restarting the computer, you will see to update the operating system. Accept the terms and click OK.
Select the drive you want to choose. Install it on the system. You can also see the details of the hard drive installed on the computer. Set up Windows and select your options. Change the time and date!
What is Raid Configuration?
Raid configuration is the most important for storing data. It will speed up the computer and can save vast amounts of data.
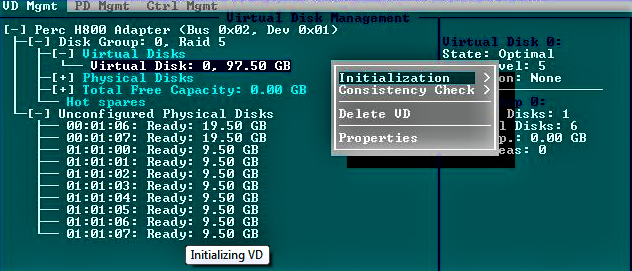
- You can use Raid 0 to prefer the speed of the computer. It will not assure you of data recovery in case of drive failure.
- Raid 1, Raid 5, Raid 6, and Raid 10 can be used for data redundancy.
- You also need a Hardware Raid controller to store business data in enormous amounts.
- Small business owners can go with Raid 1 or Raid 5 with the OS Software Raid Driver.
- The critical business and finance need to use Raid 6 or Raid 10.
- Gamers, video editors, and producers can easily use Raid 0 for the speedy performance of the device, but they must be careful about the backing up of the data.
Connectivity Procedure of Raid Connectivity
For connecting Raid to your system, your motherboard must have a built-in Raid controller. It will help you connect the hard drives and boot up the system. On the Chipset screen, you will find Raid in SATA mode. Initialize the process. Apply and Save it there. Restart the PC, and you will get Raid connectivity. You can open it up by pressing Ctrl+ R.
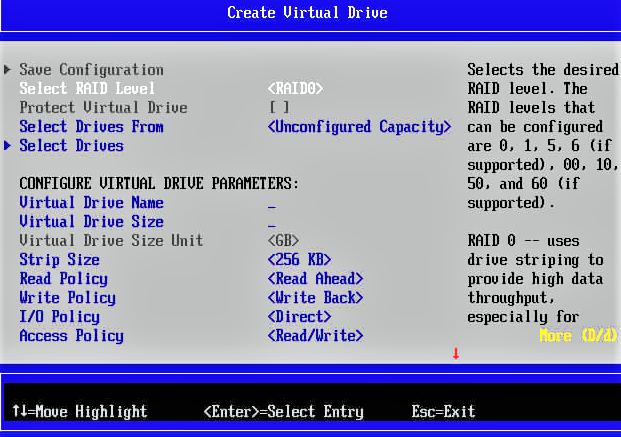
In the menu, you will pick create Array and select the hard drives for Raid configuration. Select the size of Array you want to use. Press C and the Esc+ Y for implementing the Raid setting on the system. Your computer will be restarted with Raid configuration. Now there will be a need to update BIOS.
Best Raid Supported Motherboards List
Motherboards mostly do not have built-in Raid support. There is an option to use Raid software on every motherboard. You can still use SATA ports for additional hard drives, but they are not enough. The latest motherboards are manufactured with built-in Raid support. Here you will see some best Raid motherboards.
ASUS Raid Support Motherboards
- ASUS TUF Gaming B660M plus D4 Intel Motherboard supports Raid because of its PCIe 5.0 and dual PCIe 4.0 slots. It also has Four SATA 6 GBs with USB Gen 1, Gen 2, and Gen 3 support. It is a 12th Gen Intel CPU with LGA 1700 socket.
- ASUS Prime B660M D4 Intel Motherboard is a micro ATX motherboard compatible with 12th Gen CPU with LGA 1700 socket. It also facilitates Turbo boost technology with PCIe 4.0, Realtek 1GB Ethernet, and Four SATA 6 GBs.
Gigabyte Raid Support Motherboard
- Gigabyte AMD A68, FM2 Ultra durable mothers, supports Raid. It has SATA 3 ports and USB 3.0 with DDR3 RAM. It is quite an affordable motherboard for the average user.
- Gigabyte Z590 D Ultra Durable LGA 1200 ATX motherboard is best with 10th and 11th Gen processors. It supports Raid 0, Raid 1, Raid 5, and Raid 10. Gigabyte B550 AORUSELITE motherboard supports Raid 0, Raid 1, and Raid 10. It supports 3rd Gen AMD Ryzen processors.
Raid 5 Motherboards
Raid 5 provides good storage and security of the data. It refers to the read speed but not to writing speed. Some motherboards that can go with Raid 5 are listed below.
- NZXT N5 Z690 motherboard supports Raid 5 with wireless LAN.
- ASUS PRO Q670M C LGA 1700 motherboard can also support Raid 5.
- Gigabyte X570SI AORUS Motherboard works with Raid 5.
4. Raid 6 Motherboards
Raid 6 is more reliable than Raid 5. It uses 2 drives for storage. It offers to cover up data when two drives fail. Raid 6 is safer than Raid 5. A minimum of four hard disks can be used to set up Raid 6. Some latest motherboards also have Raid 6 support.
- Gigabyte GA Z 170X and ASUS Pro Wx WRX80E motherboard support Raid 6.
We have already discussed Raid is used to recover data in case of drive failure. It also performs with the reliability to store and recover data. If there are any issues with your I/O disk, then you can use Raid. You can read and write data on multiple drives.
The hardware Raid can provide additional memory to the computer. It is suitable for large organizations and critical businesses. The hardware Raid will increase the performance of the device too. Average users can go for Software Raid, which the computer’s operating system can install.
To know about your configuration of motherboard and if it supports Raid, right-click on the Computer icon. Click on Manage. Increase its storage. Disk management will take you to Disk 0, Disk 1, etc. The disk number will guide you to the words Dynamic or Basic. If it says Basic, you do not have Raid, or if it says Dynamic, you have Raid support motherboard.
Raid uses all the available disks to store data. It can use hardware and software too. Some motherboards have built-in Raid hardware solutions. Raid is also available in Workstations. Raid provides the best storage capacity other than the primary hard disk.
This article must be beneficial for you in understanding the concept of Raid and its levels. Each of the configurations helps you in different ways to make you understand the whole system. Raid also needs a controller in the system for storing vast amounts of data. Raid software can benefit the average users, while Raid hardware is primarily for businesses and organizations.
Final Conclusion